启动过程
启动过程
基于版本 spring-boot:2.1.14.RELEAES,启动gateway项目进行观察
介绍
以下是常见的boot项目启动入口,比较核心的点就在于注解@SpringBootApplication和SpringApplication.run
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBoot2018 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBoot2018.class, args);
}
}
SpringApplication.run(String... args)结构
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 计时器
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
// 计时开始
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
// 设置java.awt.headless模式为true,Headless模式是在缺少显示屏、键盘或者鼠标时的系统配置。
configureHeadlessProperty();
// ## 获取运行监听器
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
// 发布ApplicationStartingEvent事件
listeners.starting();
try {
// 处理参数
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 准备环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
// 配置忽略bean信息 spring.beaninfo.ignore为true
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 创建应用上下文,默认org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
context = createApplicationContext();
// 获取异常报告器
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
// 准备上下文,将相关信息和上下文绑定
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// 刷新上下文,这是重点,与spring初始化的核心过程类似
refreshContext(context);
// 刷新之后的动作,暂无实现
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
// 计时结束
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
// 发布ApplicationStartedEvent事件,触发相关监听器
listeners.started(context);
// 调用运行器
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
提示
这里需要说明以下,次方法会被调用两次,一次是执行main方法时调用,另一次是在执行“准备环境”prepareEnvironment方法中会触发BootstrapApplicationListener,该方法又重新调用了run。
所以在执行prepareEnvironment时触发BootstrapApplicationListener时,会优先执行监听器触发的run方法调用,等执行完成之后,再继续执行之后的代码。所以prepareEnvironment之前的方法调用是main方法触发,BootstrapApplicationListener后触发,后面的方法则相反。
这里在分析run方法的过程中各个阶段时,并没有都针对两次运行进行分析,没特殊说明都默认为main方法调用
BootstrapApplicationListener会根据environment.getPropertySources().contains("bootstrap")判断是否执行过,不会存在递归触发的情况。
运行监听器
获取运行监听器
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[] { SpringApplication.class, String[].class };
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger,
getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args));
}
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
通过SpringFactoriesLoader去加载org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
try {
// 从META-INF/spring.factories中查询
Enumeration<URL> urls = (classLoader != null ?
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryClassName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
for (String factoryName : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue())) {
result.add(factoryClassName, factoryName.trim());
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
}
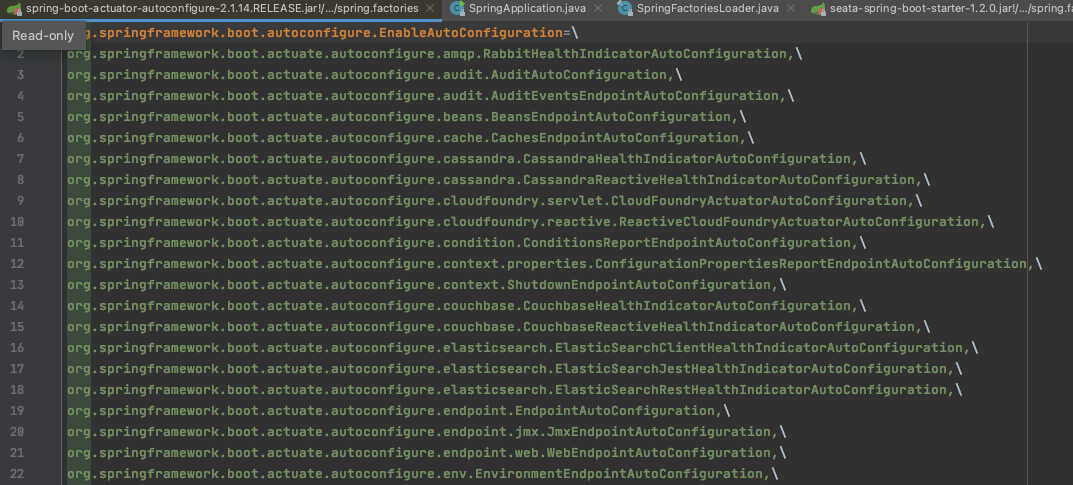
- 首先调用
loadSpringFactories(classLoader),通过classLoader从META-INF/spring.factories加载内容(如下图)。将其他中的内容存放到LinkedMultiValueMap对象中,等号左边的factoryClassName为key,等号右边的多值存放到LinkedList作为value。最后将结果存放到一个缓存对象cache中,key为当前的classloader,避免重复加载提升性能。
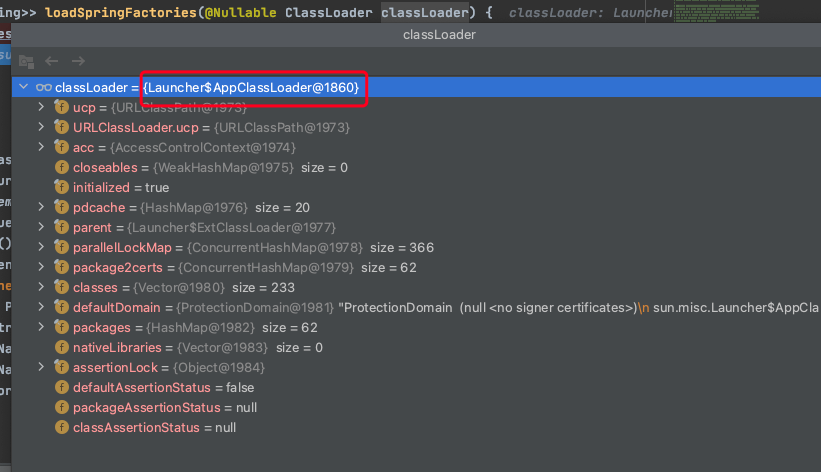
- 从上一点中计算出的结果中通过key
org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener获取所有的Spring应用运行监听器,然后排序存入SpringApplicationRunListeners中
开启监听器
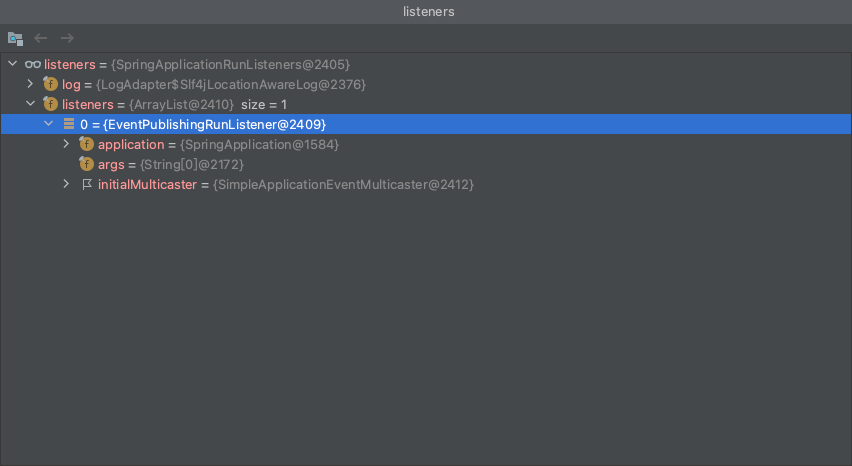
通过SpringApplicationRunListeners的starting()方法批量触发监听器
当前拥有的监听器为EventPublishingRunListener
发布启动事件
ApplicationStartingEvent
发布ApplicationStartingEvent事件,触发相关监听器(调用onApplicationEvent方法)
通过EventPublishingRunListener来组播org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationStartingEvent事件
// EventPublishingRunListener
@Override
public void starting() {
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args));
}
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
// 先获取ApplicationStartingEvent监听器然后执行事件
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
// getApplicationListeners调用retrieveApplicationListeners
retrieveApplicationListeners方法获取所有监听ApplicationStartingEvent事件的监听器
先通过
this.defaultRetriever.applicationListeners获取默认的监听器listener筛选出支持
ApplicationStartingEvent事件的监听器,加入监听器集合
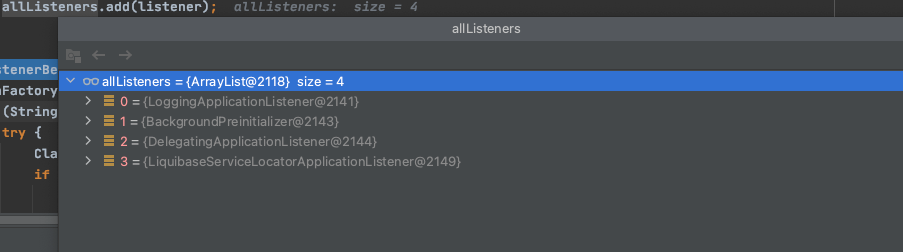
main与BootstrapApplicationListener执行时监听器是一致的。
- 如果listenerBeans存在,则根据beanName创建监听器,加入监听器集合
this.defaultRetriever初始化?
准备环境
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 设置转化服务,设置命令行参数,设置激活profile
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
// 这应该是让配置类可以获取环境信息
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 触发监听器方法(一旦环境准备好,但在ApplicationContext创建之前调用),发布`ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent`事件
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
// 将环境信息绑定至SpringApplication
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
当前所有监听ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件的监听器
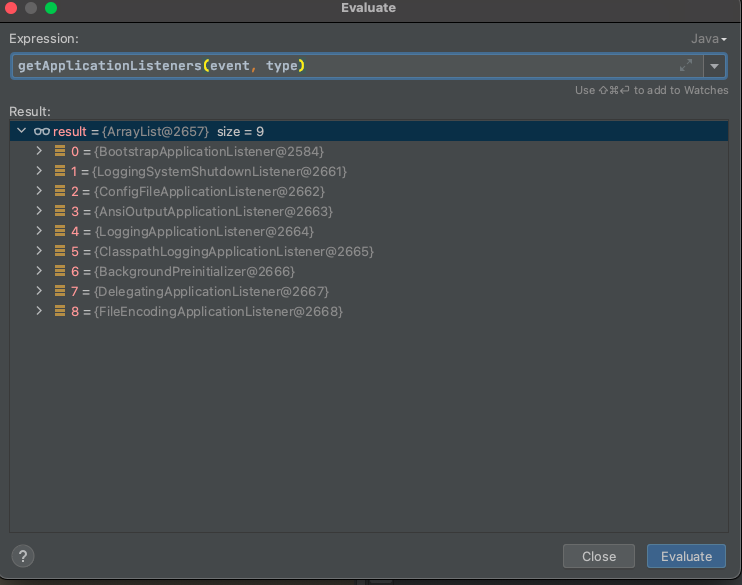
图中第一个监听器BootstrapApplicationListener需要在这里说明以下,该监听器被触发之后会再次执行SpringApplication的run方法,所以该监听器会优先于main方法进行调用创建上下文方法。
所以在prepareEnvironment之后的方法调用
创建应用上下文
context = createApplicationContext();
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, " + "please specify an ApplicationContextClass",
ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
提示
由于环境准备中会触发SpringApplicationRunListeners的environmentPrepared方法,内部会触发所有监听了ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件的监听器的onApplicationEvent方法。
listeners中包含BootstrapApplicationListener,该监听器会再次触发SpringApplication的run方法,所以该监听器会优先于main方法进行调用创建上下文方法。
此时如果没有特殊设置
BootstrapApplicationListener上下文默认创建为org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
main上下文默认创建为org.springframework.boot.web.reactive.context.AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext
就启动过程而言,后续过程准备上下文、刷新上下文、刷新上下文后置动作、发布已启动事件、调用运行器都需针对这两类上下文进行操作。
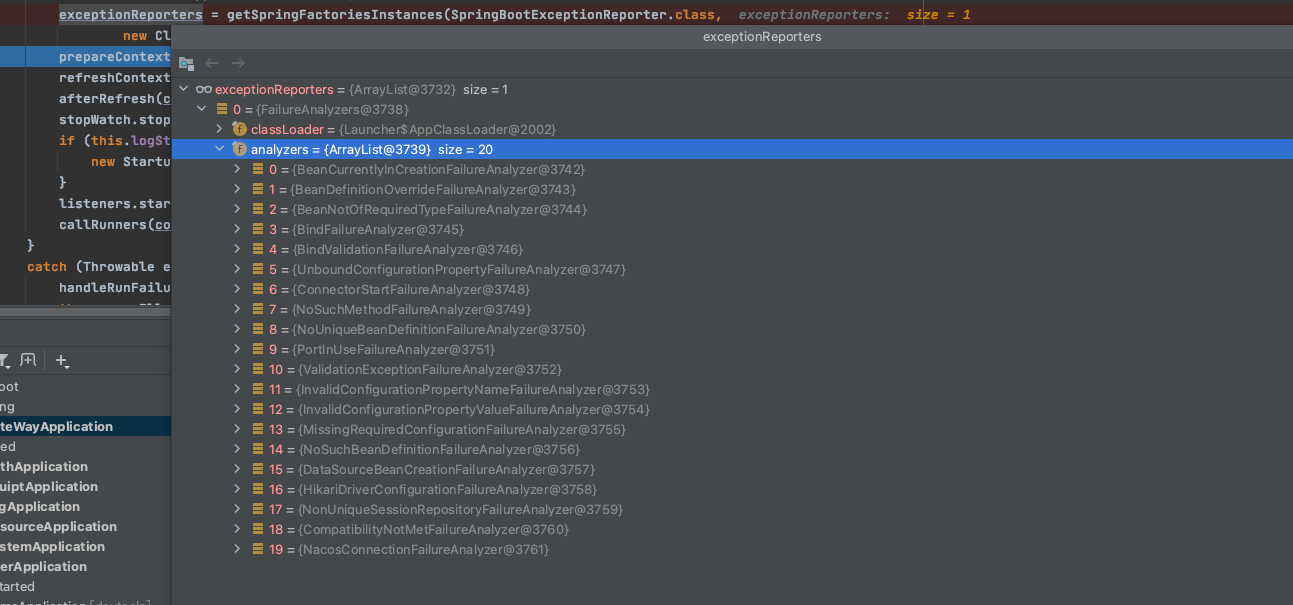
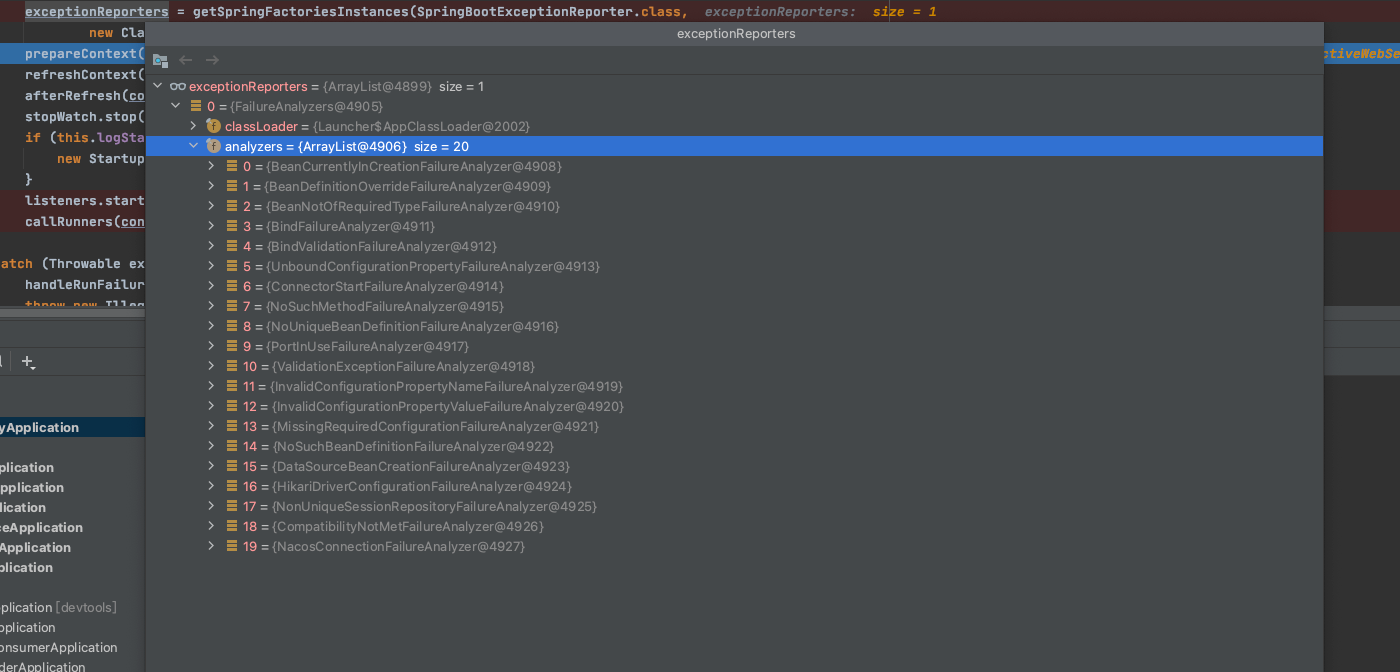
异常报告器
BootstrapApplicationListener触发
main方法触发
准备上下文
prepareContext,准备上下文,将相关信息和上下文绑定
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
// 上下文绑定环境
context.setEnvironment(environment);
// 应用上下文后置处理
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
// 在初始化完成之前,将所有的初始化器应用于上下文
applyInitializers(context);
// 发布ApplicationContextInitializedEvent事件
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
// Load the sources 载入所有来源
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
// 监听器载入上下文
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
上下文后置处理
protected void postProcessApplicationContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
if (this.beanNameGenerator != null) {
// 注册单例的beanName生成器
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton(AnnotationConfigUtils.CONFIGURATION_BEAN_NAME_GENERATOR,
this.beanNameGenerator);
}
if (this.resourceLoader != null) {
// 设置
if (context instanceof GenericApplicationContext) {
((GenericApplicationContext) context).setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
}
if (context instanceof DefaultResourceLoader) {
((DefaultResourceLoader) context).setClassLoader(this.resourceLoader.getClassLoader());
}
}
if (this.addConversionService) {
context.getBeanFactory().setConversionService(ApplicationConversionService.getSharedInstance());
}
}
替AnnotationConfigApplicationContext设置转换服务
应用初始化器Initializers
完成注册bean工厂后置处理器的工作
从META-INF/spring.factories中寻找ApplicationContextInitializer.class
也由可能通过其他方式,如:
BootstrapApplicationListener.AncestorInitializer和BootstrapApplicationListener.DelegatingEnvironmentDecryptApplicationInitializer是由事件BootstrapApplicationListener直接传递增加
PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration、EnvironmentDecryptApplicationInitializer是由事件BootstrapApplicationListener从上下文中根据类型ApplicationContextInitializer.class获取
BootstrapApplicationListener先通过SpringApplicationBuilder的run方法,创建SpringApplication并执行相关初始化操作,执行完之后在监听器后续代码还会添加Initializer,包括:BootstrapApplicationListener.AncestorInitializer、PropertySourceBootstrapConfiguration、EnvironmentDecryptApplicationInitializer、BootstrapApplicationListener.DelegatingEnvironmentDecryptApplicationInitializer
创建时机:
SpringApplication创建时
事件
protected void applyInitializers(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
for (ApplicationContextInitializer initializer : getInitializers()) {
Class<?> requiredType = GenericTypeResolver.resolveTypeArgument(initializer.getClass(),
ApplicationContextInitializer.class);
Assert.isInstanceOf(requiredType, context, "Unable to call initializer.");
initializer.initialize(context);
}
}
BootStrap调用执行时
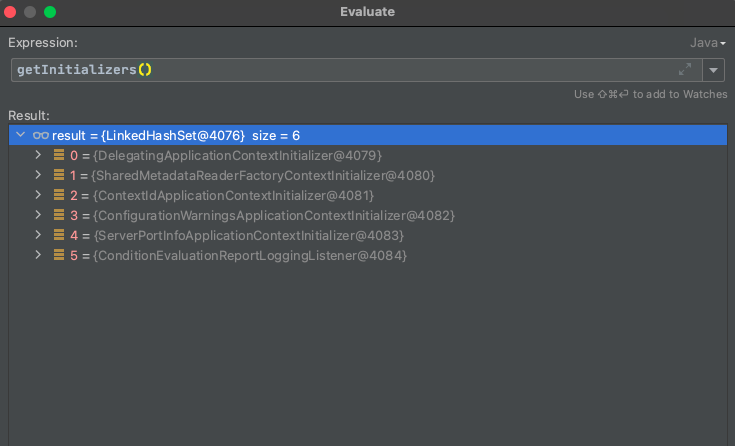
main调用执行时
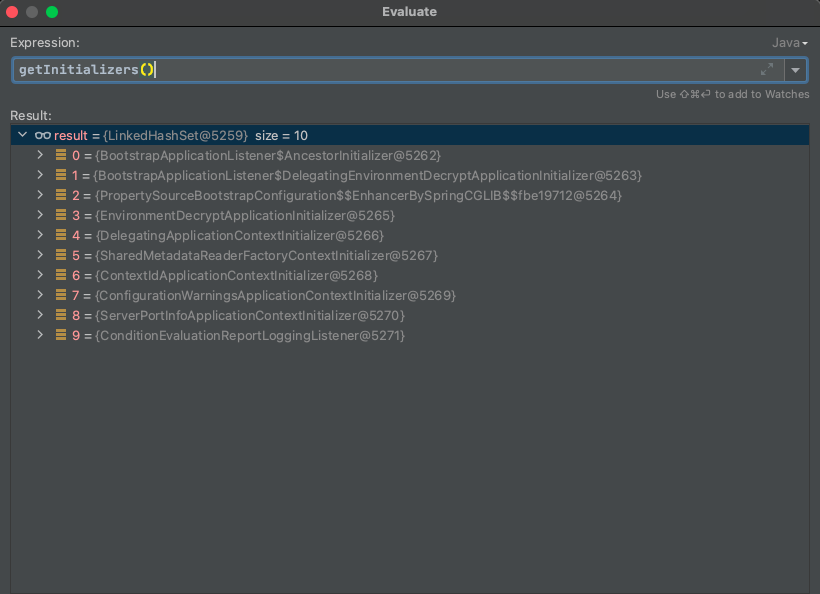
发布事件
发布ApplicationContextInitializedEvent事件
载入sources
获取所有sources
public Set<Object> getAllSources() {
Set<Object> allSources = new LinkedHashSet<>();
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.primarySources)) {
allSources.addAll(this.primarySources);
}
if (!CollectionUtils.isEmpty(this.sources)) {
allSources.addAll(this.sources);
}
return Collections.unmodifiableSet(allSources);
}
当上下文为AnnotationConfigApplicationContext时,this.primarySources = org.springframework.cloud.bootstrap.BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration
将sources载入上下文
根据sources和上下文获取bean定义加载器
载入的过程会调用AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader的register方法,将sources的内容都注册进去
注册的过程后面再讨论 TODO
protected void load(ApplicationContext context, Object[] sources) {
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loading source " + StringUtils.arrayToCommaDelimitedString(sources));
}
// 这里需要根据sources和上下文获取bean定义加载器
BeanDefinitionLoader loader = createBeanDefinitionLoader(getBeanDefinitionRegistry(context), sources);
if (this.beanNameGenerator != null) {
loader.setBeanNameGenerator(this.beanNameGenerator);
}
if (this.resourceLoader != null) {
loader.setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
}
if (this.environment != null) {
loader.setEnvironment(this.environment);
}
loader.load();
}
监听器载入上下文
public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : this.application.getListeners()) {
// 如果实现了ApplicationContextAware接口,则设置上下文
if (listener instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) listener).setApplicationContext(context);
}
// 上下文注册监听器
context.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
// 触发应用准备完成事件
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, context));
}
主要做三件事情
如果实现了
ApplicationContextAware接口,则设置上下文上下文注册监听器该监听器
触发应用准备完成事件
ApplicationPreparedEvent
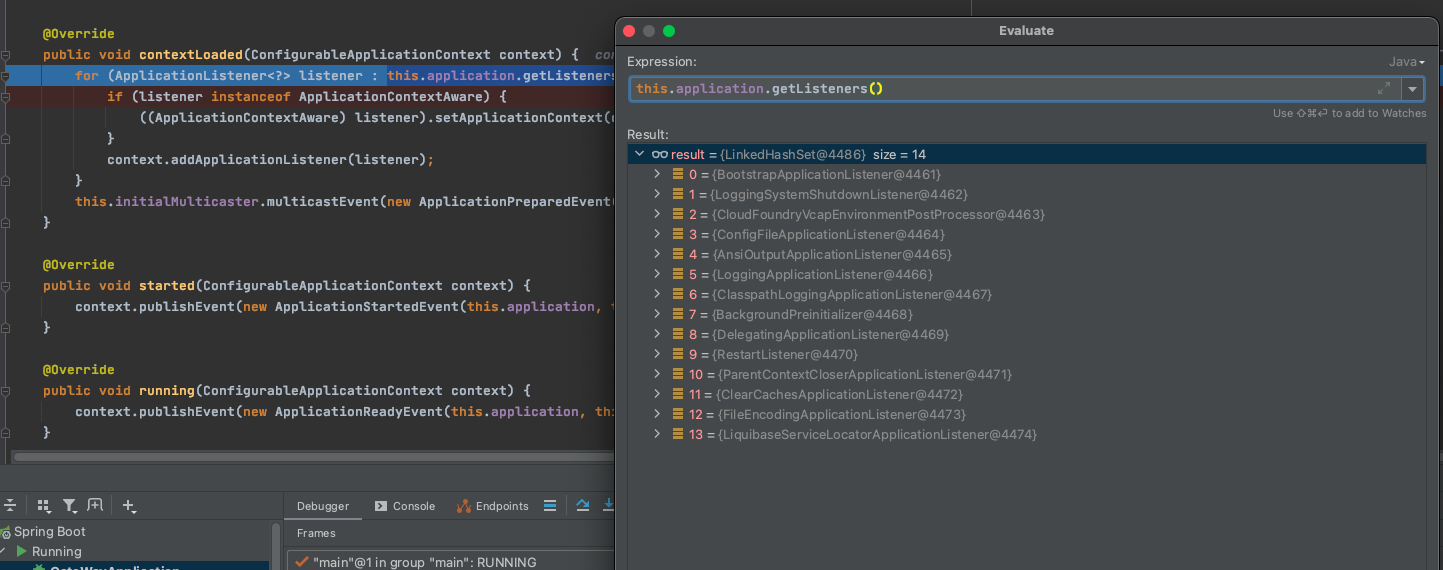
刷新上下文
初始化过程的核心,与spring初始化过程类似,调用上下文对象的refresh()方法
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
// 调用上下文对象的refresh()方法,该方法实际上在抽象类AbstractApplicationContext中
refresh(context);
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
try {
context.registerShutdownHook();
}
catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments.
}
}
}
// AbstractApplicationContext
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing. 为上下文刷新做准备
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.告诉子类去刷新内部bean工厂,bean工厂为DefaultListableBeanFactory
// 与Spring初始化不同,这里并没有做实质性的工作,而Spring在该步骤进行了BeanDefinition的加载
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. 为当前上下文准备好bean工厂
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
// 运行上下文子类中bean工厂的后置处理,默认为空实现。AnnotationConfigApplicationContext未重写此类。
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
// 调用在上下文中注册为Bean的工厂处理器,执行工厂后置处理器
// 比如BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration,执行@Import({BootstrapImportSelector.class})
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
// 注册bean后置处理器
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
// 初始化MessageSource
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
// 初始化事件多播器
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
执行工厂后置处理器
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
上下文AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对应的后置处理器为
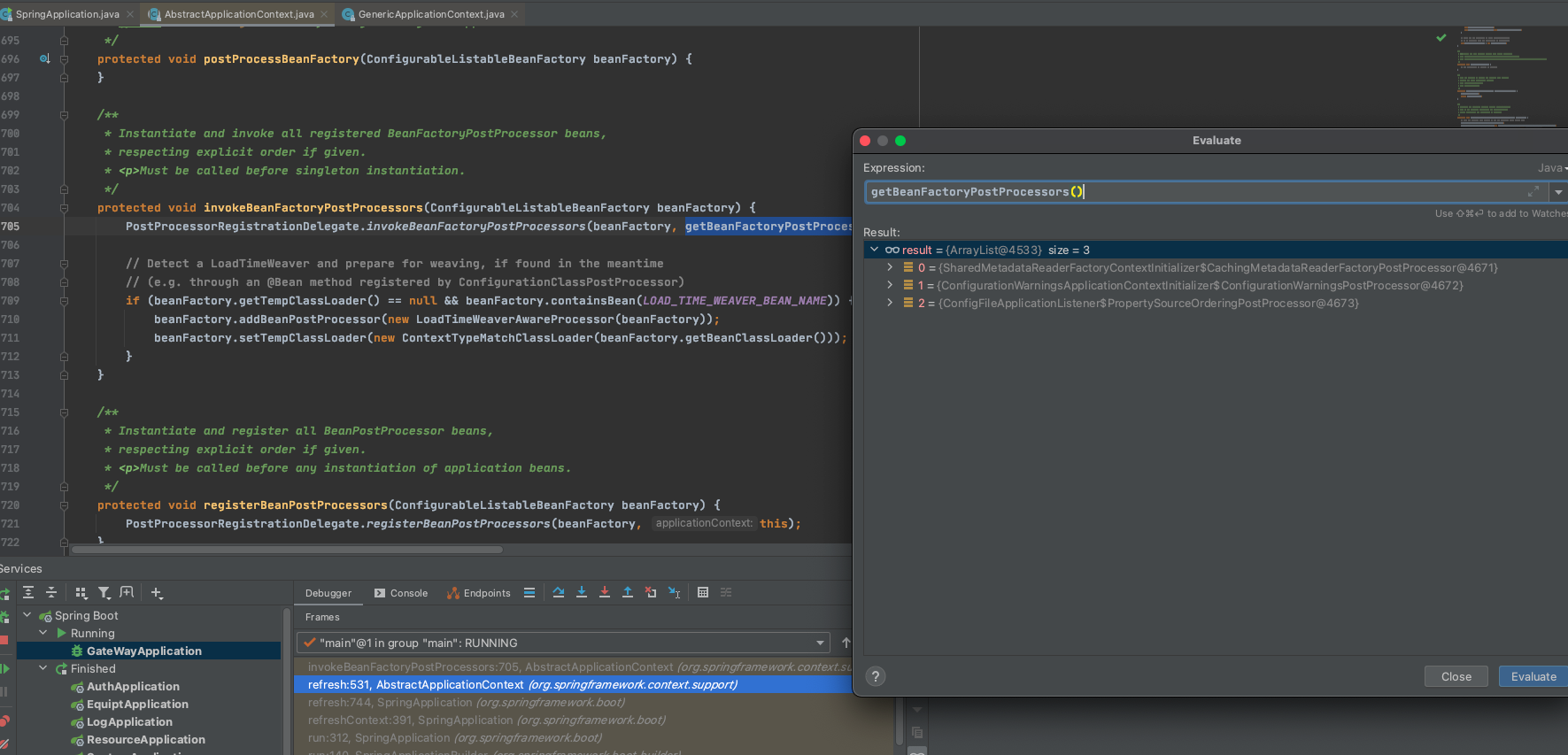
- 首先分别对这几个bean工厂后置处理器进行一些操作
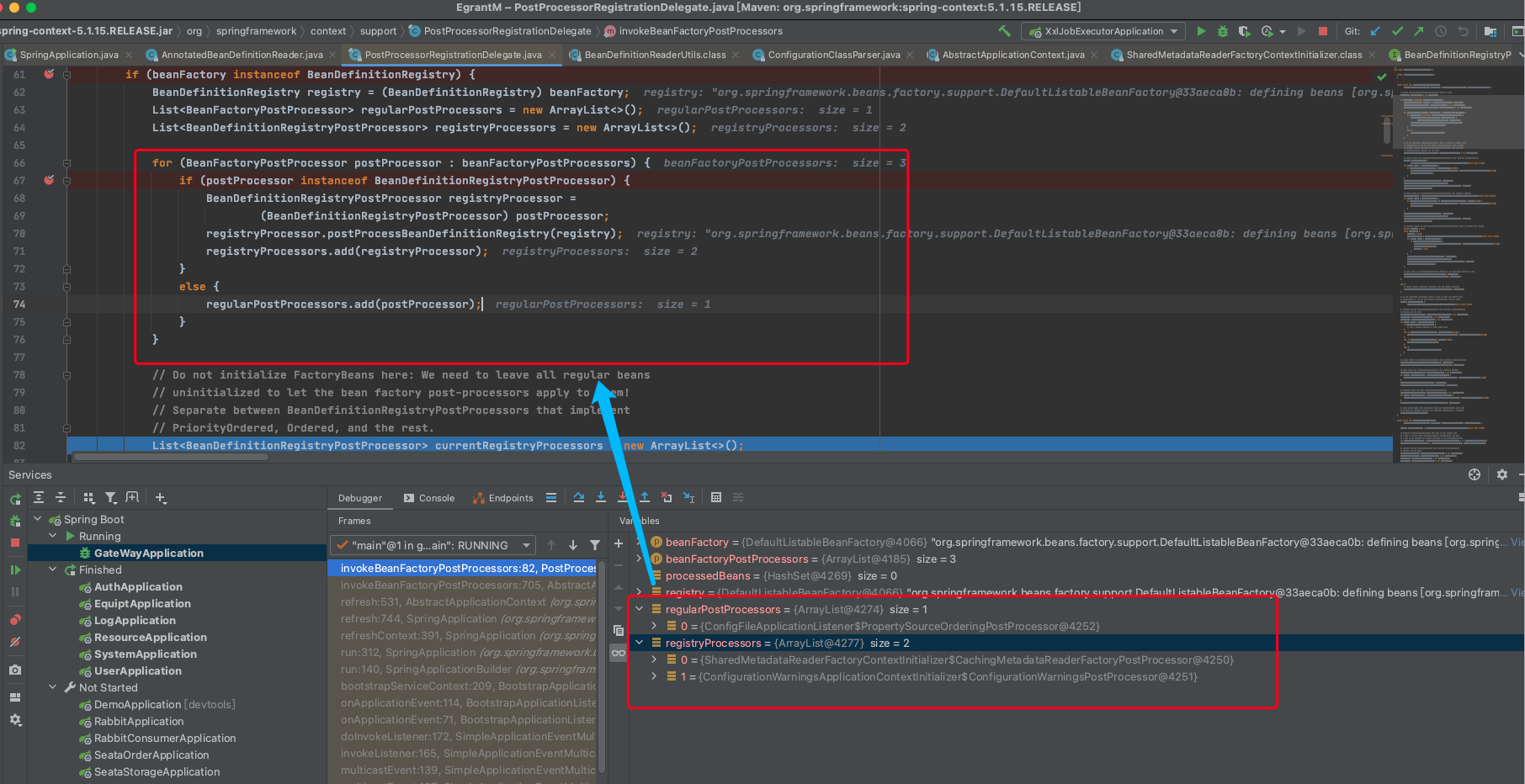
- 因为需要先调用实现了
PriorityOrdered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors,找到对应的bean进行排序后执行,然后统计到处理器数组
org.springframework.context.annotation.ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
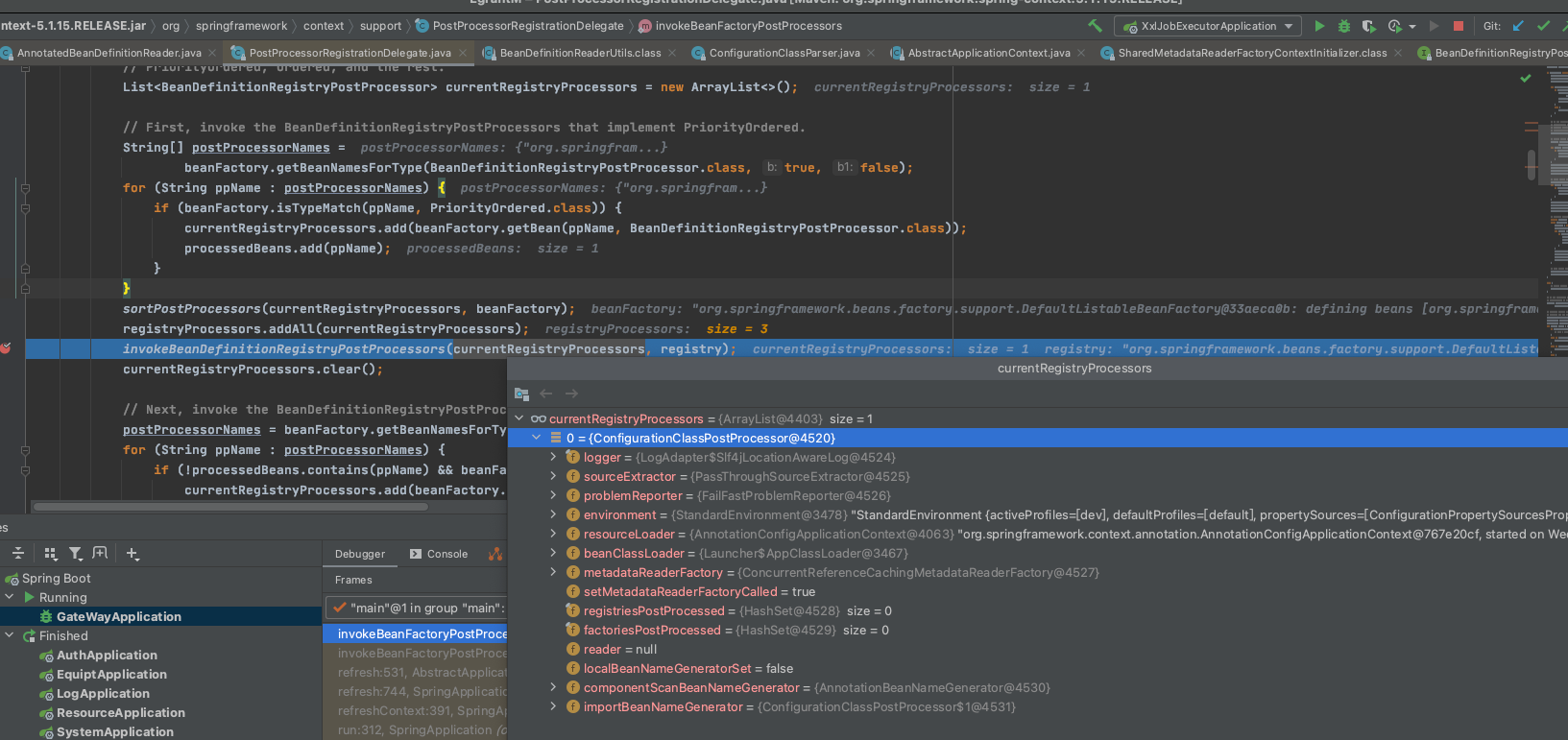
调用方法为invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
与上一点类似,寻找对应的 实现了
Ordered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors最后执行其他的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors,直到没有发现新的位置
通过
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors执行所有后置处理器的回调,也就是调用他们的postProcessBeanFactory
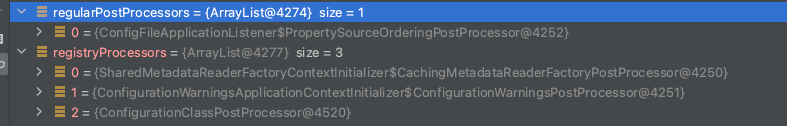
后置处理器是由初始化器Initializers来完成,也可能是通过其他方式,如监听器ConfigFileApplicationListener
刷新上下文后置动作
暂无实现
发布已启动事件
发布ApplicationStartedEvent事件,触发相关监听器
相关监听器的获取也是通过EventPublishingRunListener,详情请参考发布启动事件
调用运行器
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);
}
}
}
获取所有的ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner,排序之后调用run方法。
BootstrapApplicationListener
注册bean
BootstrapImportSelectorConfiguration
运行已经注册的工厂处理器