AOP
AOP
spring-aop:5.2.10.RELEASE
概述
Spring的的创建过程分为实例化和初始化。对于初始化而言,Spring提供了可通过BeanPostProcessor在初始化前后进行操作的机制。
创建AOP代理的过程是在初始化完成时期完成的,代码如下:
// AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
@Override
public Object applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object existingBean, String beanName)
throws BeansException {
Object result = existingBean;
for (BeanPostProcessor processor : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
Object current = processor.postProcessAfterInitialization(result, beanName);
if (current == null) {
return result;
}
result = current;
}
return result;
}AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator主要用于完成AOP代理创建的过程,由上述代码可知创建方法为postProcessAfterInitialization,其中较为关键的是wrapIfNecessary
/**
* Create a proxy with the configured interceptors if the bean is
* identified as one to proxy by the subclass.
* @see #getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean
*/
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
// 包装代理对象方法
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
// wrapIfNecessary
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}wrapIfNecessary主要逻辑:
获取拦截器-获取当前bean所配置的通知(advice)对应的拦截器,除了自定义的advice生成的拦截器,还会有Spring设置的拦截器,比如:ExposeInvocationInterceptor。如果没有配置则直接返回当前bean
创建代理对象-通过代理工厂
ProxyFactory创建代理对象
获取拦截器
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) {
List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
}
return advisors.toArray();
}创建代理对象
先看以下代码:
/**
* Create an AOP proxy for the given bean.
* @param beanClass the class of the bean
* @param beanName the name of the bean
* @param specificInterceptors the set of interceptors that is
* specific to this bean (may be empty, but not null)
* @param targetSource the TargetSource for the proxy,
* already pre-configured to access the bean
* @return the AOP proxy for the bean
* @see #buildAdvisors
*/
protected Object createProxy(Class<?> beanClass, @Nullable String beanName,
@Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
// 构建Advisor
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
// 获取代理对象
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}对象创建的过程包含以下部分:
根据拦截器集合构建Advisor集合
获取代理对象
构建Advisor
主要完成拦截器等非Advisor对象转换为Advisor接口对象的过程,这个过程中也可能会插入一些默认的拦截器
转换过程默认由DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry的wrap完成
protected Advisor[] buildAdvisors(@Nullable String beanName, @Nullable Object[] specificInterceptors) {
// Handle prototypes correctly...
Advisor[] commonInterceptors = resolveInterceptorNames();
List<Object> allInterceptors = new ArrayList<>();
if (specificInterceptors != null) {
allInterceptors.addAll(Arrays.asList(specificInterceptors));
if (commonInterceptors.length > 0) {
if (this.applyCommonInterceptorsFirst) {
allInterceptors.addAll(0, Arrays.asList(commonInterceptors));
}
else {
allInterceptors.addAll(Arrays.asList(commonInterceptors));
}
}
}
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
int nrOfCommonInterceptors = commonInterceptors.length;
int nrOfSpecificInterceptors = (specificInterceptors != null ? specificInterceptors.length : 0);
logger.trace("Creating implicit proxy for bean '" + beanName + "' with " + nrOfCommonInterceptors +
" common interceptors and " + nrOfSpecificInterceptors + " specific interceptors");
}
Advisor[] advisors = new Advisor[allInterceptors.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < allInterceptors.size(); i++) {
// 拦截器对象转换为Advisor对象
advisors[i] = this.advisorAdapterRegistry.wrap(allInterceptors.get(i));
}
return advisors;
}获取代理对象
通过在ProxyFactory中设置当前对象所有的Advisor、原对象等其他配置信息,然后调用getProxy方法返回代理对象
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
return createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader);
}
protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy() {
if (!this.active) {
activate();
}
return getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this);
}
/**
* Return the AopProxyFactory that this ProxyConfig uses.
*/
public AopProxyFactory getAopProxyFactory() {
return this.aopProxyFactory;
}createAopProxy()会获取代理工厂,并根据之前向ProxyFactory设置的配置信息创建Aop代理AopProxy
这里的代理工厂一般是DefaultAopProxyFactory,createAopProxy会根据判断使用Cglib或者Jdk代理结合之前向ProxyFactory配置的信息创建对象。
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}调用getProxy获取代理对象时会使用增强器org.springframework.cglib.proxy.Enhancer将所有的Advisor和一些其他的配置信息设置进代理对象(下方有Cglib对应的完整代码),Enhancer会完成对普通bean的增强功能
//CglibAopProxy
@Override
public Object getProxy(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Creating CGLIB proxy: " + this.advised.getTargetSource());
}
try {
Class<?> rootClass = this.advised.getTargetClass();
Assert.state(rootClass != null, "Target class must be available for creating a CGLIB proxy");
Class<?> proxySuperClass = rootClass;
if (rootClass.getName().contains(ClassUtils.CGLIB_CLASS_SEPARATOR)) {
proxySuperClass = rootClass.getSuperclass();
Class<?>[] additionalInterfaces = rootClass.getInterfaces();
for (Class<?> additionalInterface : additionalInterfaces) {
this.advised.addInterface(additionalInterface);
}
}
// Validate the class, writing log messages as necessary.
validateClassIfNecessary(proxySuperClass, classLoader);
// Configure CGLIB Enhancer...
Enhancer enhancer = createEnhancer();
if (classLoader != null) {
enhancer.setClassLoader(classLoader);
if (classLoader instanceof SmartClassLoader &&
((SmartClassLoader) classLoader).isClassReloadable(proxySuperClass)) {
enhancer.setUseCache(false);
}
}
enhancer.setSuperclass(proxySuperClass);
enhancer.setInterfaces(AopProxyUtils.completeProxiedInterfaces(this.advised));
enhancer.setNamingPolicy(SpringNamingPolicy.INSTANCE);
enhancer.setStrategy(new ClassLoaderAwareGeneratorStrategy(classLoader));
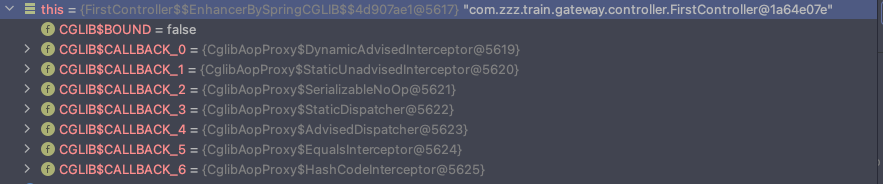
Callback[] callbacks = getCallbacks(rootClass);
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[callbacks.length];
for (int x = 0; x < types.length; x++) {
types[x] = callbacks[x].getClass();
}
// fixedInterceptorMap only populated at this point, after getCallbacks call above
// 设置回调
enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(
this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));
enhancer.setCallbackTypes(types);
// Generate the proxy class and create a proxy instance.
return createProxyClassAndInstance(enhancer, callbacks);
}
catch (CodeGenerationException | IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new AopConfigException("Could not generate CGLIB subclass of " + this.advised.getTargetClass() +
": Common causes of this problem include using a final class or a non-visible class",
ex);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
// TargetSource.getTarget() failed
throw new AopConfigException("Unexpected AOP exception", ex);
}
}设置代理回调过滤器(ProxyCallbackFilter)
上述代码中 enhancer.setCallbackFilter(new ProxyCallbackFilter(this.advised.getConfigurationOnlyCopy(), this.fixedInterceptorMap, this.fixedInterceptorOffset));
ProxyCallbackFilter会在执行Class<?> proxyClass = enhancer.createClass();时被调用accept方法。
构建回调对象集合Callback
Callback对象是Spring根据之前获取的Advisor所生成的,此对象会被加入到生成的代理对象中,用于后续代码调用时候的拦截作用。
提示
Spring默认使用JDK动态代理来创建代理对象(包括5.x版本)
SpringBoot 2.x 开始,为了解决使用 JDK 动态代理可能导致的类型转化异常而默认使用CGLIB,如果需要默认使用 JDK 动态代理可以通过配置项spring.aop.proxy-target-class=false来进行修改,proxyTargetClass配置已无效。
SpringBoot 2.x是通过org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.aop.AopAutoConfiguration来实现Aop的自动配置
Advisor是如何初始化的?
先看之前出现过的AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator中的获取方法
// AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, @Nullable TargetSource targetSource) {
List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
}
return advisors.toArray();
}
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}查找的过程主要分为两步:
查找所有候选的Advisor
过滤出对当前bean生效的Advisor
过滤的过程相对来说简单,主要看下所有候选的Advisor是怎么来的,通过下面的代码可用大体得知:
根据父类的规则来获取
从bean工厂
BeanFactoryAspectJAdvisorsBuilder获取,这里记录了包含@Aspect的类和其内部配置的Advisor
@Override
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {
// Add all the Spring advisors found according to superclass rules.
List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();
// Build Advisors for all AspectJ aspects in the bean factory.
if (this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null) {
advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());
}
return advisors;
}为什么会执行回调?
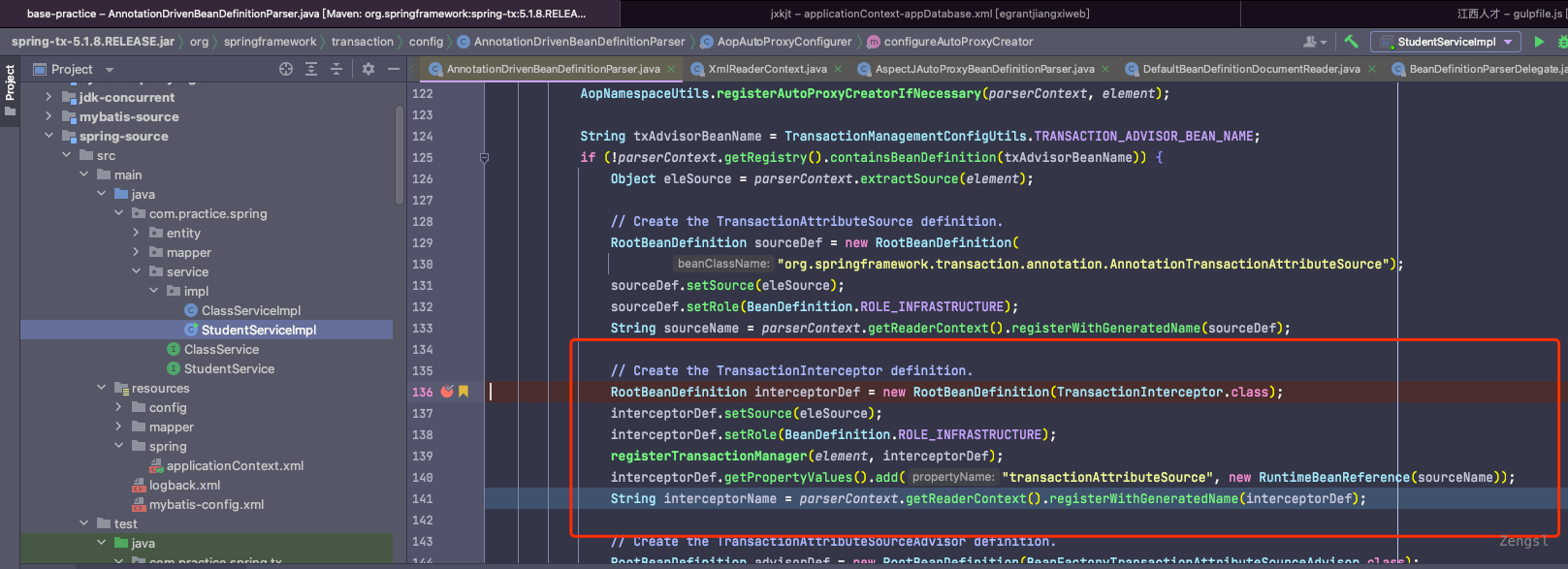
事务拦截器
注册位置