容器初始化过程
容器初始化过程
提示
以Spring3.2源码进行阅读,主要是xml的配置方式
概要
项目集成spring一般会在web.xml中配置ContextLoaderListener和contextConfigLocation
ContextLoaderListener是用来完成Spring上下文初始化的关键
contextConfigLocation参数是用来指定spring配置文件的路径
因为是扫描xml的配置方式,那么使用的应用上下文为XmlWebApplicationContext
<!--Spring启动的监听器-->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>classpath:spring/applicationContext*.xml</param-value>
</context-param>ContextLoaderListener的contextInitialized是用来初始化上下文的入口
/**
* Initialize the root web application context.
*/
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) {
this.contextLoader = createContextLoader();
if (this.contextLoader == null) {
this.contextLoader = this;
}
this.contextLoader.initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext());
}ContextLoader的configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext方法完成上下文初始化工作,其中调用的wac.refresh()是整个初始化的核心
protected void configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext wac, ServletContext sc) {
if (ObjectUtils.identityToString(wac).equals(wac.getId())) {
// The application context id is still set to its original default value
// -> assign a more useful id based on available information
String idParam = sc.getInitParameter(CONTEXT_ID_PARAM);
if (idParam != null) {
wac.setId(idParam);
}
else {
// Generate default id...
if (sc.getMajorVersion() == 2 && sc.getMinorVersion() < 5) {
// Servlet <= 2.4: resort to name specified in web.xml, if any.
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getServletContextName()));
}
else {
wac.setId(ConfigurableWebApplicationContext.APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ID_PREFIX +
ObjectUtils.getDisplayString(sc.getContextPath()));
}
}
}
// Determine parent for root web application context, if any.
ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(sc);
wac.setParent(parent);
wac.setServletContext(sc);
String initParameter = sc.getInitParameter(CONFIG_LOCATION_PARAM);
if (initParameter != null) {
wac.setConfigLocation(initParameter);
}
customizeContext(sc, wac);
// refresh是整个初始化的核心
wac.refresh();
}refresh方法由AbstractApplicationContext提供,里面包含了“刷新内部bean工厂”、“注册Bean的前置处理器”、“初始化事件多播器”、“初始化bean”、“注册监听器”、“完成bean工厂初始化”和“发布事件”等工作。
下文将会整个过程逐步分析
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
}
}刷新准备工作
由prepareRefresh()完成
刷新获取bean工厂
由ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();完成
此过程将完成BeanDefinitions的加载,加载过程整体预览
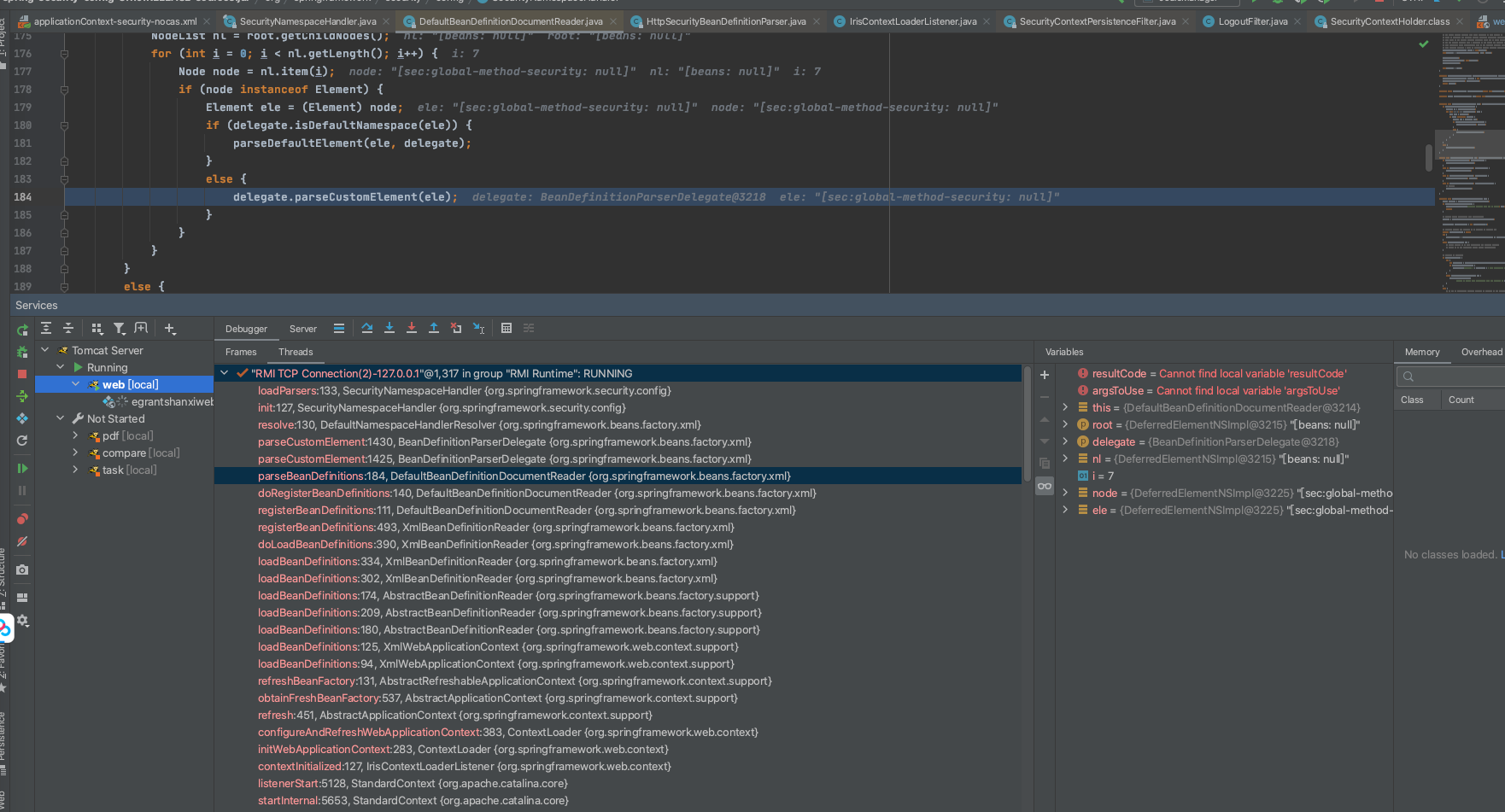
loadBeanDefinitions
refreshBeanFactory()调用loadBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitionReader)
- 此方法遍历contextConfigLocation所配置的application*.xml路径,使用
XmlBeanDefinitionReader的loadBeanDefinitions加载所对应路径的文件
将配置文件转化为Resource对象,如果配置文件采用的是通配符*的表达方式则会返回Resource数组
对每一个Resource对象对象进行加载,整个加载过程都是由
XmlBeanDefinitionReader完成由doLoadBeanDefinitions调用registerBeanDefinitions完成bean注册过程。此过程会创建
ReaderContext,其包含了配置文件中的命名空间解析器namespaceHandlerResolver和XmlBeanDefinitionReader等其他信息
public int registerBeanDefinitions(Document doc, Resource resource) throws BeanDefinitionStoreException {
BeanDefinitionDocumentReader documentReader = createBeanDefinitionDocumentReader();
documentReader.setEnvironment(this.getEnvironment());
int countBefore = getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount();
// createReaderContext获取配置文件对应的命名空间解析器
documentReader.registerBeanDefinitions(doc, createReaderContext(resource));
return getRegistry().getBeanDefinitionCount() - countBefore;
}- 由
doRegisterBeanDefinitions完成进一步等解析调用和准备工作,此过程会创建一个delegate委托器BeanDefinitionParserDelegate
protected void doRegisterBeanDefinitions(Element root) {
String profileSpec = root.getAttribute(PROFILE_ATTRIBUTE);
if (StringUtils.hasText(profileSpec)) {
Assert.state(this.environment != null, "environment property must not be null");
String[] specifiedProfiles = StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(profileSpec, BeanDefinitionParserDelegate.MULTI_VALUE_ATTRIBUTE_DELIMITERS);
if (!this.environment.acceptsProfiles(specifiedProfiles)) {
return;
}
}
// any nested <beans> elements will cause recursion in this method. In
// order to propagate and preserve <beans> default-* attributes correctly,
// keep track of the current (parent) delegate, which may be null. Create
// the new (child) delegate with a reference to the parent for fallback purposes,
// then ultimately reset this.delegate back to its original (parent) reference.
// this behavior emulates a stack of delegates without actually necessitating one.
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate parent = this.delegate;
// 创建BeanDefinitionParserDelegate
this.delegate = createHelper(readerContext, root, parent);
preProcessXml(root);
// bean定义解析调用
parseBeanDefinitions(root, this.delegate);
postProcessXml(root);
this.delegate = parent;
}- 遍历xml配置文件中的节点,使用delegate委托器
BeanDefinitionParserDelegate进行解析
通过delegate委托器的isDefaultNamespace方法判断根节点或者子节点是否是默认命名空间。如果不是默认节点,那么调用delegate的parseCustomElement方法。否则调用DefaultBeanDefinitionDocumentReader中的parseDefaultElement
默认命名空间为BEANS_NAMESPACE_URI = "http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
parseCustomElement解析非默认的XML元素
public BeanDefinition parseCustomElement(Element ele, BeanDefinition containingBd) {
String namespaceUri = getNamespaceURI(ele);
// 获取命名空间对应的处理类,NamespaceHandlerResolver中维护了一个命名空间和对应处理类的映射关系的map
NamespaceHandler handler = this.readerContext.getNamespaceHandlerResolver().resolve(namespaceUri);
if (handler == null) {
error("Unable to locate Spring NamespaceHandler for XML schema namespace [" + namespaceUri + "]", ele);
return null;
}
return handler.parse(ele, new ParserContext(this.readerContext, this, containingBd));
}从元素中获取命名空间地址,如
http://www.springframework.org/schema/security获取readerContext
通过readerContext中
DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver所维护的命名空间与NamespaceHandler类的映射关系维护对象handlerMappings,获取该命名空间地址对应的NamespaceHandler类,创建实例并进行init初始化然后返回。http://www.springframework.org/schema/security对应的处理类是class org.springframework.security.config.SecurityNamespaceHandler以SecurityNamespaceHandler为例子,init()调用loadParsers()初始化该命名空间下面的所有元素和对应的BeanDefinitionParser的映射关系,存放至一个map中
private void loadParsers() { // Parsers parsers.put(Elements.LDAP_PROVIDER, new LdapProviderBeanDefinitionParser()); parsers.put(Elements.LDAP_SERVER, new LdapServerBeanDefinitionParser()); parsers.put(Elements.LDAP_USER_SERVICE, new LdapUserServiceBeanDefinitionParser()); parsers.put(Elements.USER_SERVICE, new UserServiceBeanDefinitionParser()); parsers.put(Elements.JDBC_USER_SERVICE, new JdbcUserServiceBeanDefinitionParser()); parsers.put(Elements.AUTHENTICATION_PROVIDER, new AuthenticationProviderBeanDefinitionParser()); parsers.put(Elements.GLOBAL_METHOD_SECURITY, new GlobalMethodSecurityBeanDefinitionParser()); parsers.put(Elements.AUTHENTICATION_MANAGER, new AuthenticationManagerBeanDefinitionParser()); parsers.put(Elements.METHOD_SECURITY_METADATA_SOURCE, new MethodSecurityMetadataSourceBeanDefinitionParser()); // Only load the web-namespace parsers if the web classes are available try { ClassUtils.forName("org.springframework.security.web.FilterChainProxy", getClass().getClassLoader()); parsers.put(Elements.DEBUG, new DebugBeanDefinitionParser()); parsers.put(Elements.HTTP, new HttpSecurityBeanDefinitionParser()); parsers.put(Elements.HTTP_FIREWALL, new HttpFirewallBeanDefinitionParser()); parsers.put(Elements.FILTER_INVOCATION_DEFINITION_SOURCE, new FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSourceParser()); parsers.put(Elements.FILTER_SECURITY_METADATA_SOURCE, new FilterInvocationSecurityMetadataSourceParser()); parsers.put(Elements.FILTER_CHAIN, new FilterChainBeanDefinitionParser()); filterChainMapBDD = new FilterChainMapBeanDefinitionDecorator(); } catch(Throwable t) { logger.error("Failed to load required web classes", t); } }调用NamespaceHandler的parse方法进行解析
根据xml元素调用其对应的BeanDefinitionParser的parse方法进行解析,比如
<sec:http中http对应的解析器为HttpSecurityBeanDefinitionParser每一个元素的解析器所做工作都不同,这里不做更深入的分析。
命名空间处理器映射
handlerMappings与DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver是绑定在一起的,handlerMappings的初始化也就在其创建过程中
protected XmlReaderContext createReaderContext(Resource resource) {
if (this.namespaceHandlerResolver == null) {
// 创建默认命名空间处理器
this.namespaceHandlerResolver = createDefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver();
}
return new XmlReaderContext(resource, this.problemReporter, this.eventListener,
this.sourceExtractor, this, this.namespaceHandlerResolver);
}创建DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver调用的构造器包含classLoader和handlerMappingsLocation两个参数
classLoader是WebappClassLoader
handlerMappingsLocation使用的是默认值是"META-INF/spring.handlers"
public static final String DEFAULT_HANDLER_MAPPINGS_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.handlers";
public DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver(ClassLoader classLoader) {
this(classLoader, DEFAULT_HANDLER_MAPPINGS_LOCATION);
}
public DefaultNamespaceHandlerResolver(ClassLoader classLoader, String handlerMappingsLocation) {
Assert.notNull(handlerMappingsLocation, "Handler mappings location must not be null");
this.classLoader = (classLoader != null ? classLoader : ClassUtils.getDefaultClassLoader());
this.handlerMappingsLocation = handlerMappingsLocation;
}在调用resolve方法的时候会调用getHandlerMappings()获取处理器映射,在所有jar包中收集META-INF/spring.handlers内容
private Map<String, Object> getHandlerMappings() {
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
synchronized (this) {
if (this.handlerMappings == null) {
try {
Properties mappings =
PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadAllProperties(this.handlerMappingsLocation, this.classLoader);
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("Loaded NamespaceHandler mappings: " + mappings);
}
Map<String, Object> handlerMappings = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object>(mappings.size());
CollectionUtils.mergePropertiesIntoMap(mappings, handlerMappings);
this.handlerMappings = handlerMappings;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable to load NamespaceHandler mappings from location [" + this.handlerMappingsLocation + "]", ex);
}
}
}
}
return this.handlerMappings;
}如在spring-beans-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar包中找到spring.handlers
# spring-beans-3.2.0.RELEASE.jar中spring.handlers内容如下
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/c=org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.SimpleConstructorNamespaceHandler
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/p=org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.SimplePropertyNamespaceHandler
http\://www.springframework.org/schema/util=org.springframework.beans.factory.xml.UtilNamespaceHandler注意
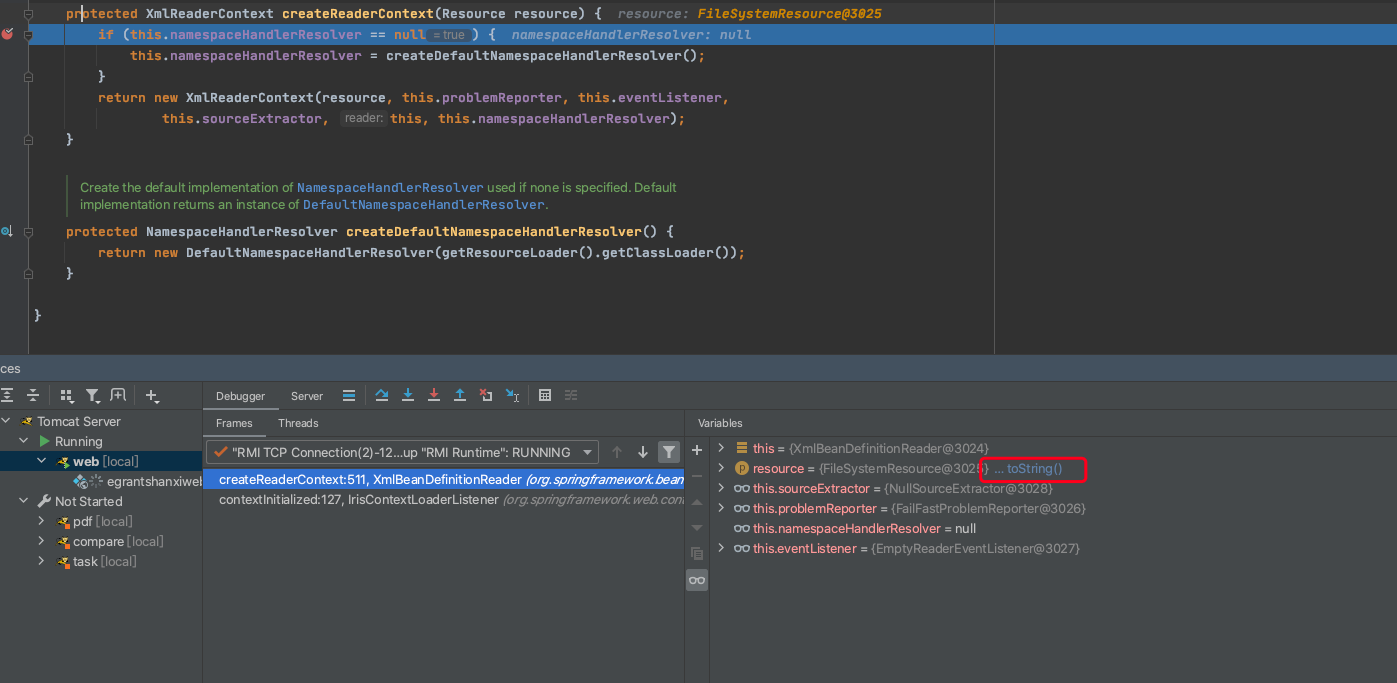
最初通过IDEA等工具进行调试等时候并没有发现进入getHandlerMappings()中的断点
通过观察代码发现getHandlerMappings()除了在上文提到的resolve方法中调用,还在toString方法中调用了。
修改IDEA中Java的Debugger的设置,去除勾选Enable toString()object view
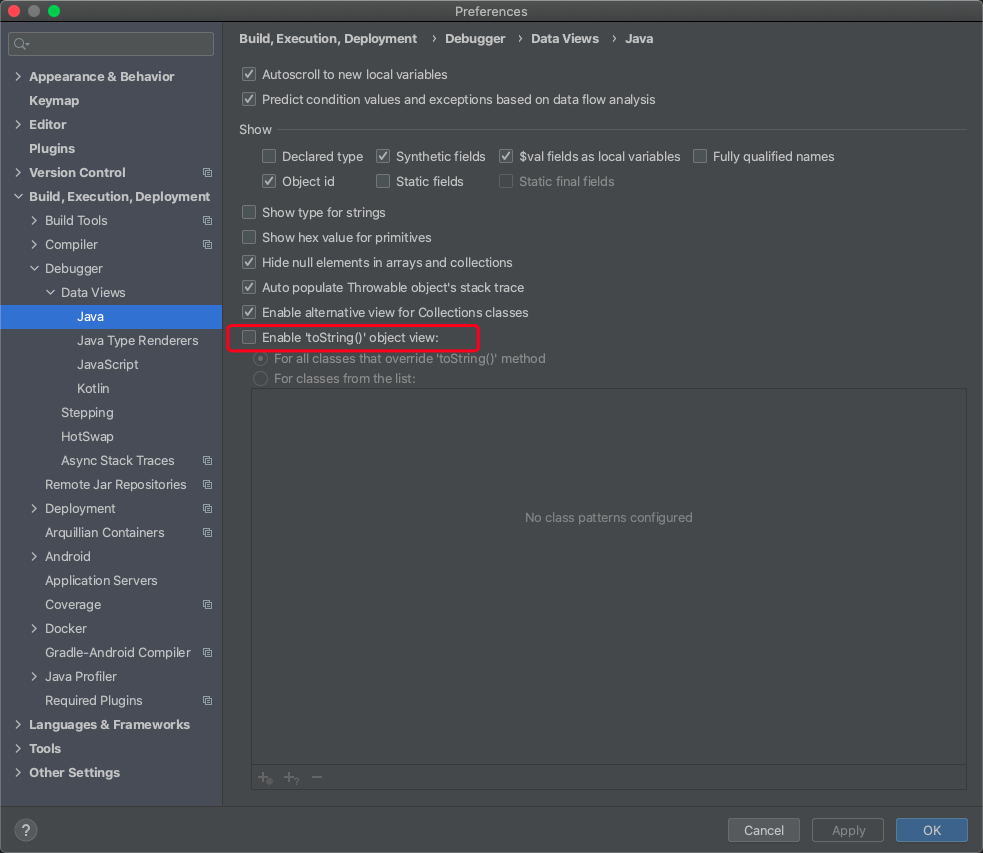
修改之后重新启动项目,能够成功进入断点
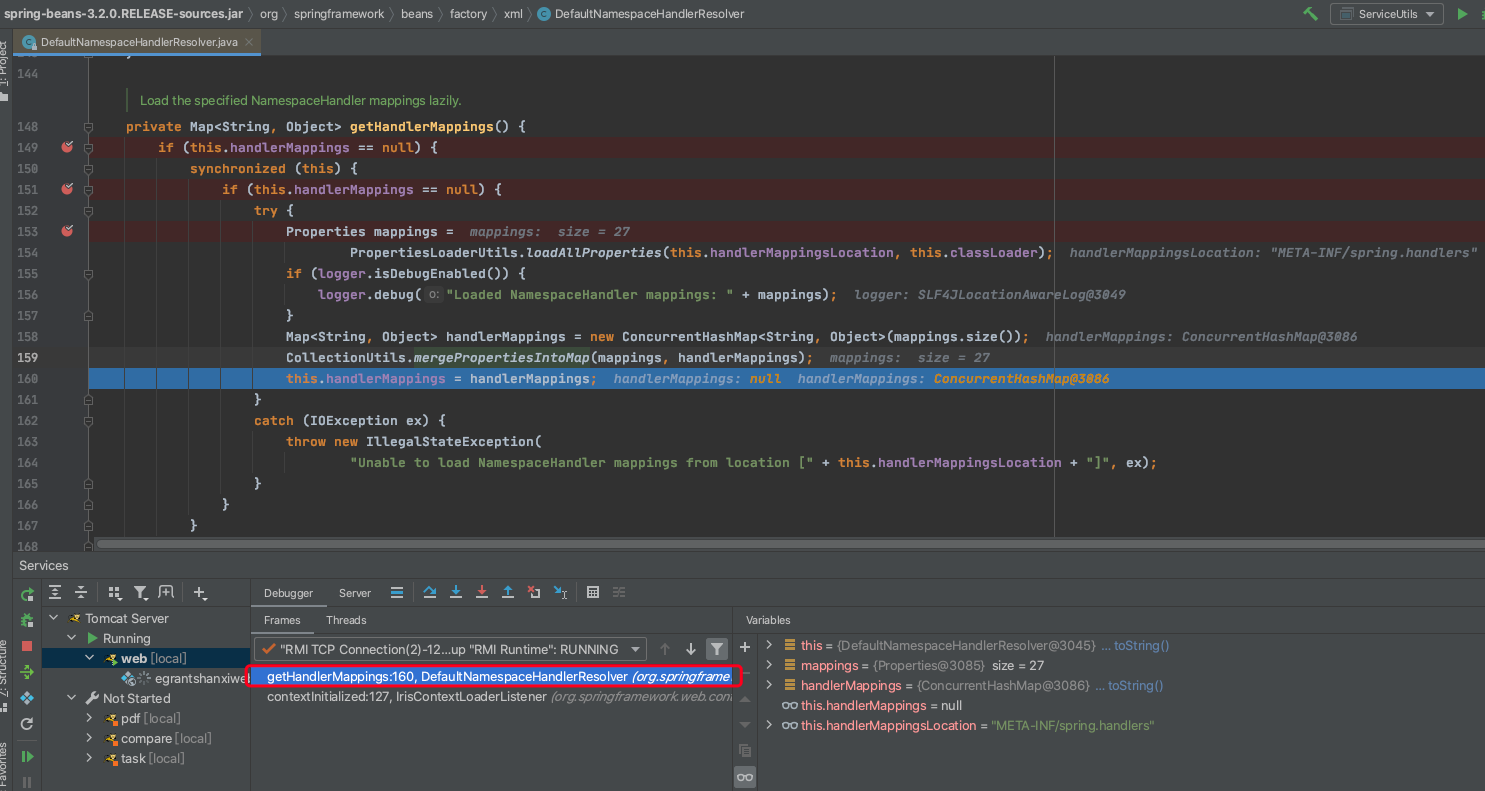
Enable toString()object view配置在调试时候的区别就是查看变量是否直接调用toString显示内容,还是手动调用
勾选
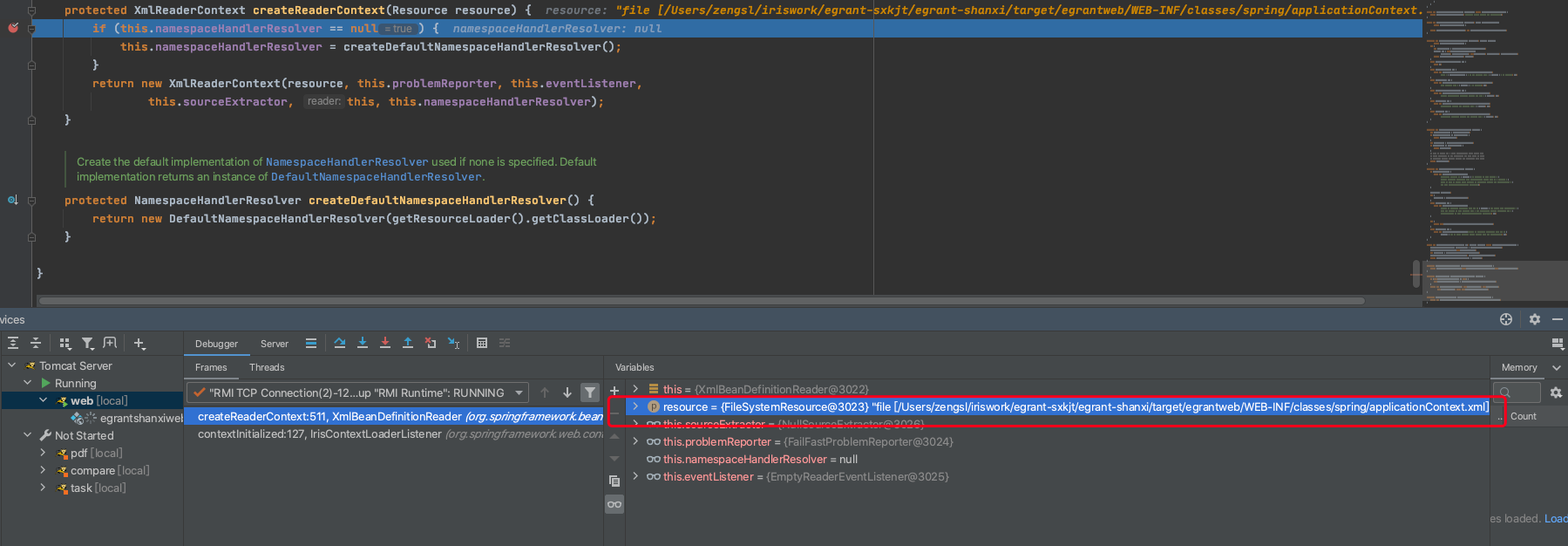
取消勾选
finishBeanFactoryInitialization
调用BeanPostProcess#postProcessBeforeInitialization -> 创建Bean-> @PostConstruct标记的方法 ->BeanPostProcess#postProcessAfterInitialization
Bean获取/创建
Spring 5.3.28
doGetBean-> createBean-> doCreateBean -> createBeanInstance -> instantiateBean -> getInstantiationStrategy().instantiate
根据getInstantiationStrategy判断是通过Cglib还是JDK代理来创建Bean实例,一般使用的策略是SimpleInstantiationStrategy。
如果是没有特殊设置:实现接口的类就通过JDK默认代理,否则使用Cglib
注意
代理对象创建之后还没有结束,后续会根据是否有AOP的需求来判断是否需要通过cglib增强。例如:@Transactional注解会使得bean通过AOP让cglib增强Bean
@Override
public Object instantiate(RootBeanDefinition bd, @Nullable String beanName, BeanFactory owner) {
// Don't override the class with CGLIB if no overrides.
if (!bd.hasMethodOverrides()) {
Constructor<?> constructorToUse;
synchronized (bd.constructorArgumentLock) {
constructorToUse = (Constructor<?>) bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod;
if (constructorToUse == null) {
final Class<?> clazz = bd.getBeanClass();
if (clazz.isInterface()) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "Specified class is an interface");
}
try {
if (System.getSecurityManager() != null) {
constructorToUse = AccessController.doPrivileged(
(PrivilegedExceptionAction<Constructor<?>>) clazz::getDeclaredConstructor);
}
else {
constructorToUse = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor();
}
bd.resolvedConstructorOrFactoryMethod = constructorToUse;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanInstantiationException(clazz, "No default constructor found", ex);
}
}
}
return BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructorToUse);
}
else {
// Must generate CGLIB subclass.
return instantiateWithMethodInjection(bd, beanName, owner);
}
}@Async所标记的类是在AsyncAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessAfterInitialization中给Bean增加切面,切面会在AsyncAnnotationAdvisor中做好,可以参考@EnableAsync。
